'Reptile Recon': Silent Push uses IP diversity queries to map out CryptoChameleon fast flux IOFAs. Hundreds of domains, IPs, and ASNs discovered

CryptoChameleon is a phishing kit first discovered in February 2024. As of publication, the identity of CryptoChameleon’s creator remains elusive.
The kit is used by unknown threat actors to harvest usernames, passwords, password reset URLs, and photo IDs from employees and customers’ mobile devices.
Silent Push Threat Analysts have conducted a wide-ranging research campaign that has revealed a large amount of CryptoChameleon fast flux Indicators of Future Attack (IOFAs) targeting Binance, Coinbase and FCC users, and a host of other platforms, including:
- Apple iCloud
- Gemini
- Kraken
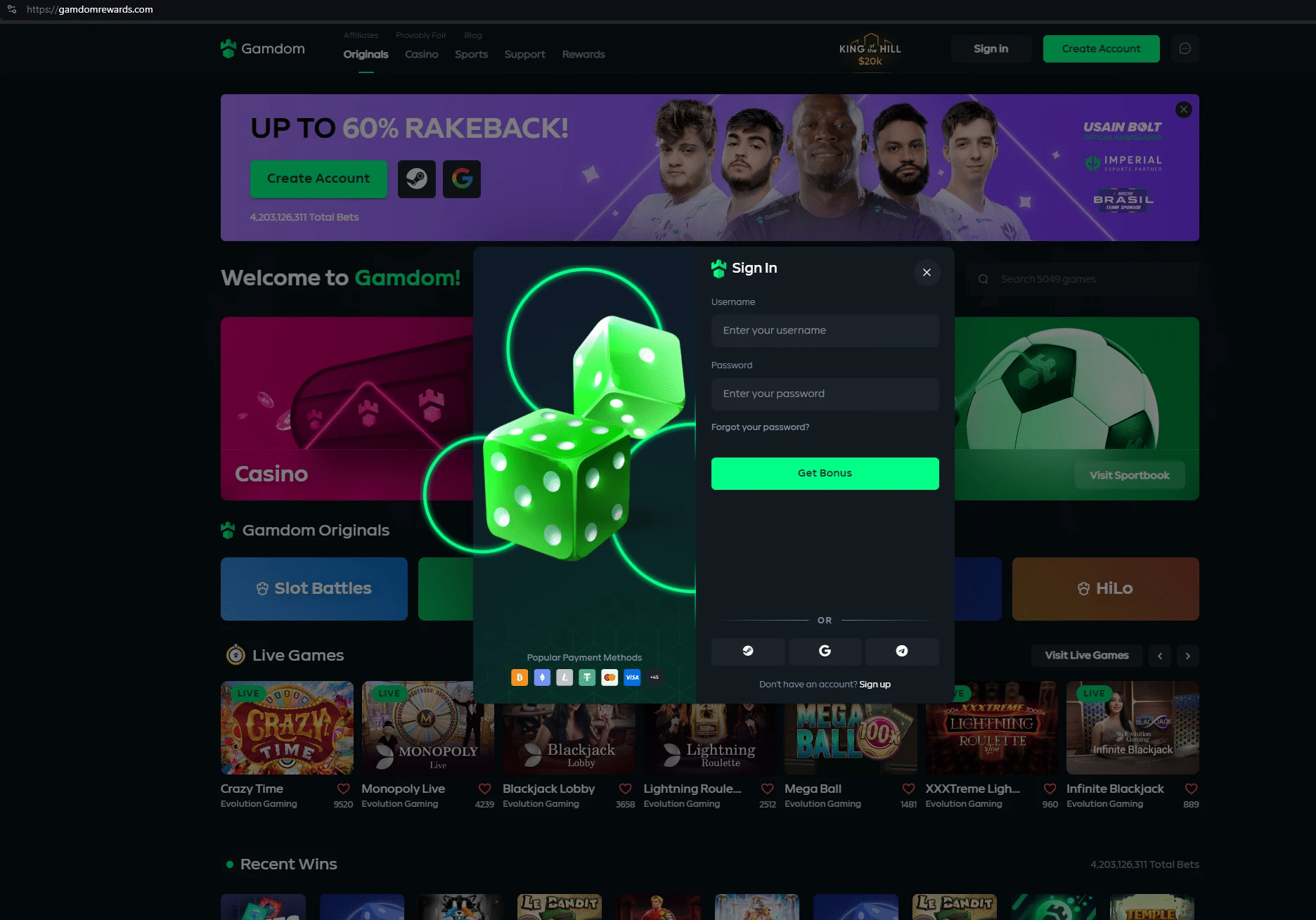
- Gamdom
- Ledger
- Swan Bitcoin
- Trezor Hardware Wallet
- Uphold
- Nexo Crypto
- Shake Pay Crypto
Background
On 6th February 2024, Silent Push analysts noticed malicious activity targeting the FCC, and reported it confidentially to CISA.
Subsequent research, published by cloud security vendor Lookout, referenced the same domain as our FCC report, which we now know to be CryptoChameleon infrastructure.
Initial reports noted the targeting of employees at the FCC, Binance and Coinbase, among others, in sophisticated email, SMS, and voice phishing attacks.
CryptoChameleon TTPs
A phishing kit can broadly be defined as a group of tools and files that work together to propagate phishing activity, and quickly deploy infrastructure.
CryptoChameleon phishing activity is propagated using a range of DNS-based and on-page TTPs.
DNSPod nameservers
Our research has discovered that CryptoChameleon makes almost exclusive use of DNSPod[.]com nameservers.
DNSPod are a self-proclaimed “intelligent DNS provider” that’s been used by botnets and bullet-proof hosting operators to propagate malicious activity for a number of years, with an estimated 30% of its infrastructure engaged in malicious activity, according to a recent Unit42 report.
DNSPod is owned by Tencent Cloud, and is based out of China.
Fast flux techniques
CryptoChameleon uses DNSPod nameservers to engage in fast flux evasion techniques that allow threat actors to quickly cycle through large amounts of IPs linked to a single domain name.
Fast flux allows CryptoChameleon infrastructure to evade traditional countermeasures, and significantly reduces the operational value of legacy point-in-time IOCs.
For more information on fast flux techniques, read our Gamaredon report.
Additional TTPs
Silent Push has also tracked a number of additional TTPs that we aren’t able to divulge in a public blog, for OPSEC reasons.
These variables are linked to the deployment of phishing domains, and form a behavioural fingerprint that allows for quick and easy monitoring of all associated infrastructure.
Silent Push Enterprise users have access to a CryptoChameleon TLP Amber report that reveals these additional measures, along with the specific queries and parameters we’ve used to uncover CryptoChameleon infrastructure, and automated mitigation steps, including dedicated domain and IP feeds.
Phishing kit behaviour
Analysis of the phishing kit indicates the ability to impersonate many different brands, across a range of sectors.
Our research aligns with other public research, which states that CryptoChameleon has separate phishing kits targeting public sector organizations.
The CryptoChameleon phishing kit copies the exact branding of legitimate websites and landing pages, with some key differences that allow the kit to evade standard countermeasures.
CryptoChameleon targets
CryptoChameleon phishing pages contain slices of data that detail the C2 server that’s being used to intercept a user’s personal information, and the organizations that are being targeted.
Analyzing one such domain – lookoutsucks[.]com (likely a parody of Lookout[.]com – the research group that was first to publicize information about the phishing kit), we can see the following companies listed:
- Yahoo
- Outlook
- Gemini
- Kraken
- Apple / iCloud
- Binance
- Uphold
- Lastpass
- Google/Gmail
- AOL
These details are stored alongside password reset prompts, sign-in prompts, OTP prompts, and 2FA flows that target any user who interacts with the domain.
CryptoChameleon phishing pages
Here’s a few screenshots that show CryptoChameleon phishing infrastructure across various websites.
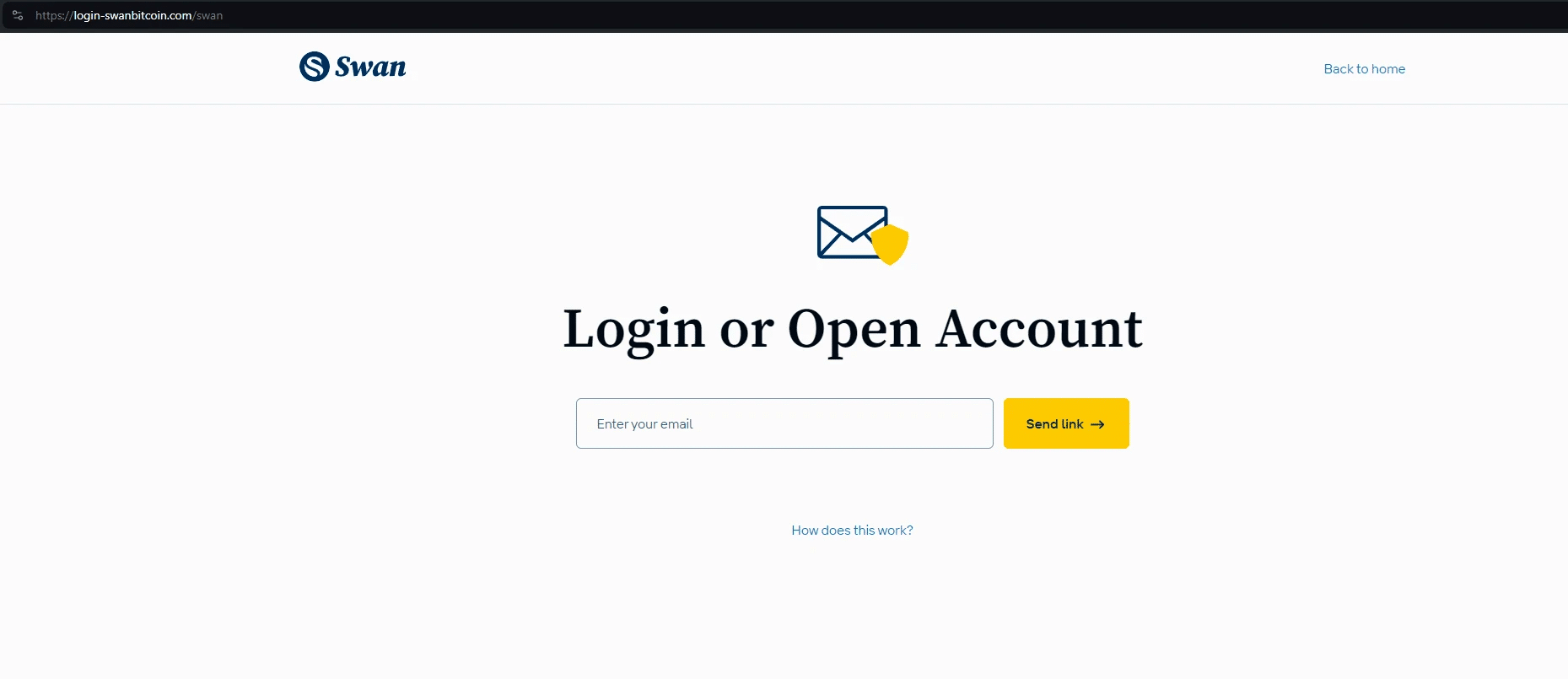
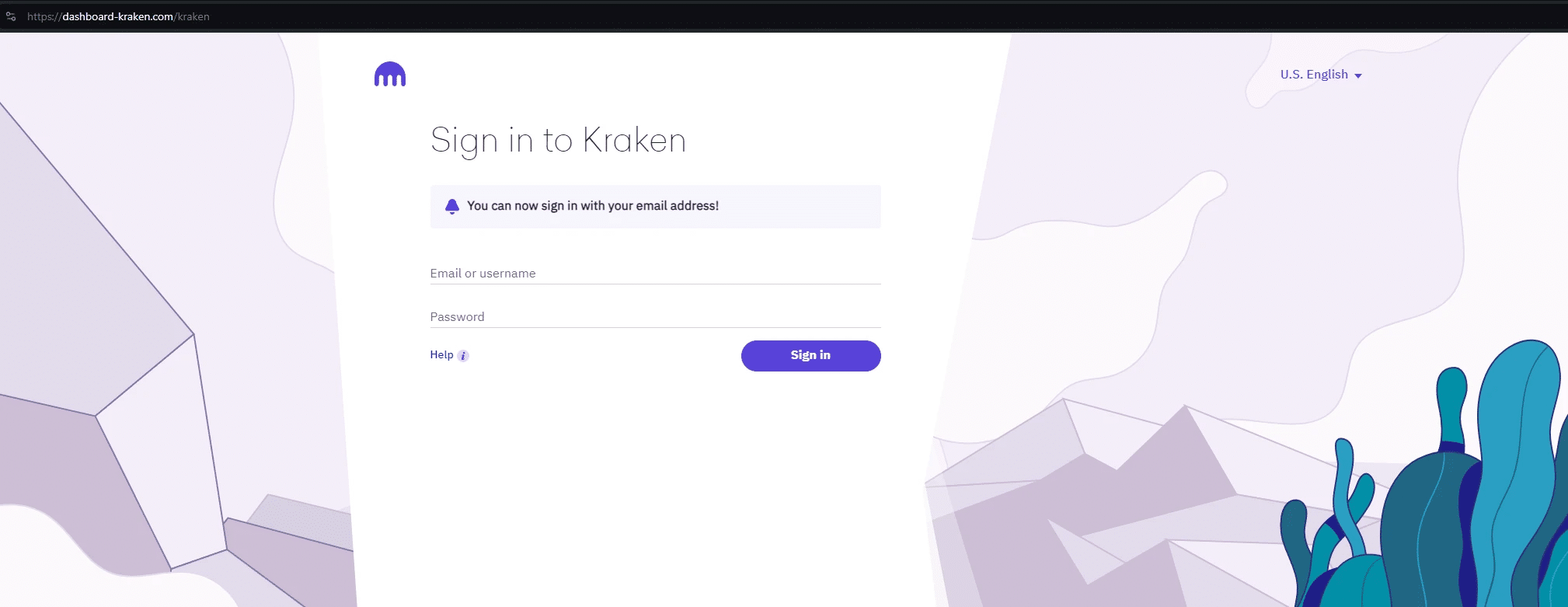
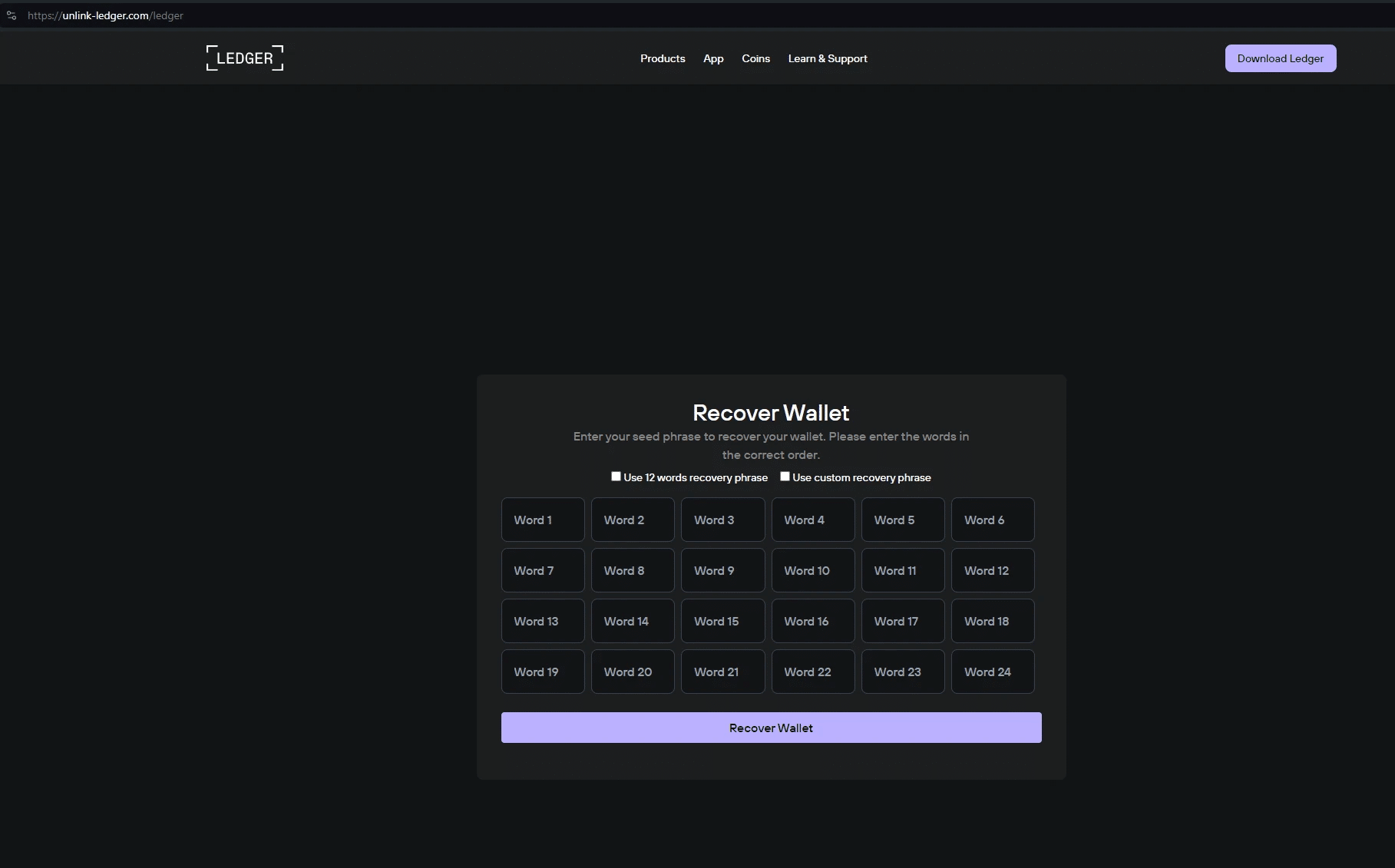
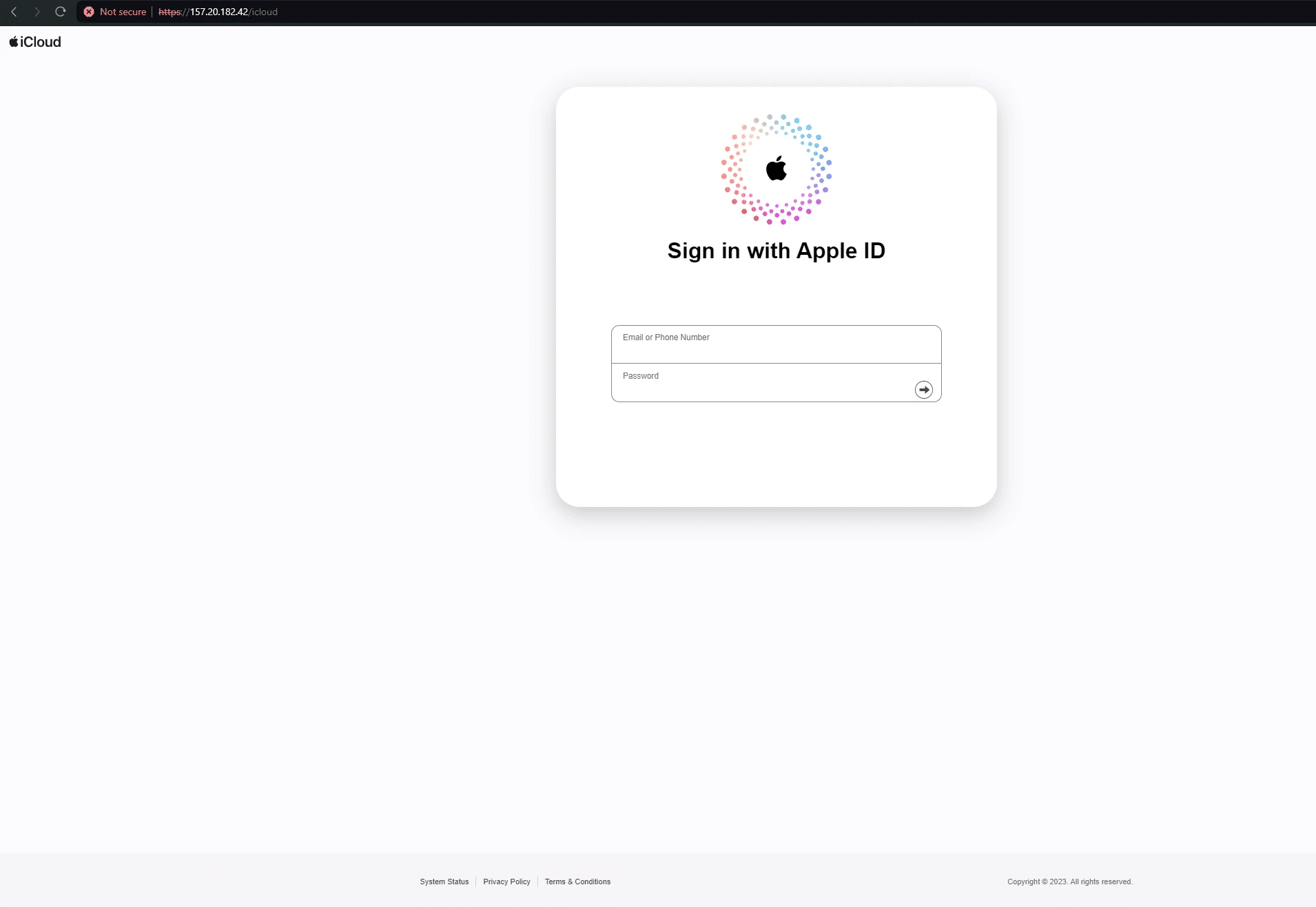
Traversing CryptoChameleon’s DNSPod infrastructure
We started by focusing our attention on DNSPod[.]com – the largest DNS provider in China, known to host a range of malicious infrastructure.
To traverse CryptoChameleon fast flux infrastructure, we executed an IP diversity query using *.dnspod[.]com nameservers as a primary parameter, and a range of secondary parameters informed by what we already know about CryptoChameleon’s deployment methods.
The full list of parameters are available in the aforementioned TLP Amber report.
Silent Push IP diversity queries return a list of IP addresses that a domain or URL has pointed to over a period of time, giving us a wealth of information that we used to map out associated infrastructure.
Analyzing the results
Silent Push DNS queries are built upon a first-party database that puts the emphasis on tracking the underlying infrastructure (nameservers, ASNs etc.) involved in an attack, rather than legacy IOCs that are the mainstay of most security teams’ brand defense workflows.
This allows defenders to anticipate and block pre-weaponized infrastructure by creating an automated early warning system that evaluates a domain or IP based in its relationship with a hosting provider or ASN.
Our IP diversity search allowed us to pinpoint numerous AS names and numbers that are actively involved in propagating CryptoChameleon attacks across the globe.
AS Names
- VDSina: Russian host
- Sannikov Kirill Vladimirovich (aka SANNIKOV): Russian host
- TIMEWEB-AS: Russian host
- Garant-Park-Internet LLC (aka GARANT): Russian host
- ALIBABA: Chinese host
AS numbers
- AS29470 JSC Retnet: Russia
- AS212441 Cloud Assets LLC: Russia
- AS212441 Cloud Assets LLC: Russia
- AS35278 Sprinthost LLC: Russia
Discovering associated domains
Our query returned 83 domains (as of writing) that are visibly similar to previous CryptoChameleon infrastructure, such as these domains targeting Coinbase:
- 76153-coinbse[.]com
- 81758-coinbse[.]com
- 81920-coinbse[.]com
- 81926-coinbse[.]com
- 81958-coinbse[.]com
- 826298-coinbse[.]com
- 83216-coinbse[.]com
- 837613-coinbse[.]com
- 83956-coinbse[.]com
Our team then analyzed the domains found via the DNSPod nameserver filtering process, and executed a Web Scanner query using a common set of characteristics, that allowed us to scan for matching infrastructrure.
CryptoChameleon infrastructure ownership
CryptoChamelon appears to control all the domains hosted on 188.68.221[.]152, and several private IP ranges where 95% of the domains follow similar patterns, with the others being more random but potentially still owned by the same operators.
The phishing kit also controls all the domains on the following IPs:
- 5.188.88[.]11
- 84.38.181[.]13
- 45.131.41.244
- 185.251.88[.]223
- 158.160.156[.]135
Here’s a sample of IPs containing CryptoChameleon-controlled infrastructure, where many of the domains are mapped to multiple IP ranges:
- 213.226.112[.]47 – 68 domains
- 78.153.149[.]108 – 68 domains
- 77.221.140[.]195 – 69 domains
- 45.151.232[.]72 – 133 domains
- 45.151.232[.]64 – 127 domains
- 45.151.232[.]66 – 48 domains
- 195.58.51[.]185 – 114 domains
- 185.185.71[.]105 – 103 domains
- 31.41.44[.]243 – 108 domains
- 5.188.88[.]229 – 66 domains
- 5.188.88[.]112 – 85 domains
- 87.251.79[.]177 – 82 domains
- 185.185.70[.]94 – 128 domains
- 5.188.88[.]34 – 102 domains
- 141.98.235[.]115 – 32 domains
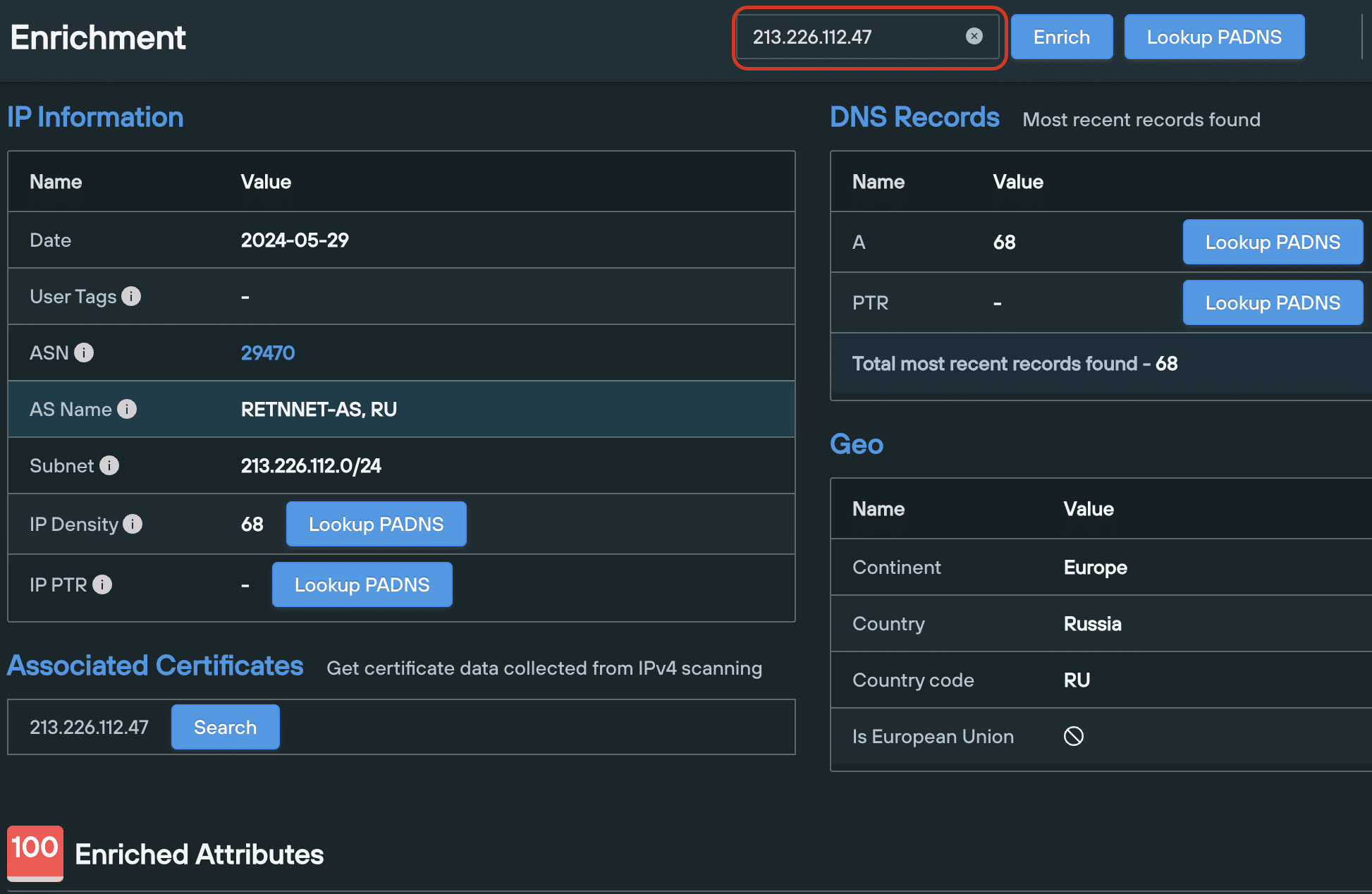
Using Silent Push to combat CryptoChameleon
All domains and IPs gathered from our research are populated in two dedicated CryptoChameleon IOFA feeds, which are constantly updated using the queries and scans discussed in this blog.
Enterprise users can use our API endpoints to feed CryptoChameleon IOFAs into their existing security stack, or access a time-limited API URL that returns a live data set.
Enterprise users can also use our TLP Amber report to pinpoint hostile ASNs and nameservers involved in CryptoChameleon activity.
Community and Enterprise users have access to a range of IP diversity queries – along with our Web Scanner – that allow security teams to quickly join the dots between billions of disparate data points, and form a complete picture of CryptoChameleon TTPs.
Register for Community Edition
Silent Push Community Edition is a free threat hunting and cyber defense platform featuring a range of advanced offensive and defensive lookups, web content queries, and enriched data types, that we used to track CryptoChameleon phishing activity.
Click here to sign-up for a free Community Edition account.
IOFA sample
A full list of CryptoChameleon IOFAs are available as part of a Silent Push Enterprise subscription, via two dedicated IOFA feeds and a TLP Amber report.
IPs
- 5.188.88[.]11
- 84.38.181[.]13
- 45.131.41.244
- 185.251.88[.]223
- 158.160.156[.]135
- 213.226.112[.]47
- 78.153.149[.]108
- 77.221.140[.]195
- 45.151.232[.]72
- 45.151.232[.]64
- 45.151.232[.]66
- 195.58.51[.]185
- 185.185.71[.]105
- 31.41.44[.]243
- 5.188.88[.]229
- 5.188.88[.]112
- 87.251.79[.]177
- 185.185.70[.]94
- 5.188.88[.]34
- 141.98.235[.]115
Hosting services
- AS29470 JSC Retnet: Russia
- AS212441 Cloud Assets LLC: Russia
- AS212441 Cloud Assets LLC: Russia
- AS35278 Sprinthost LLC: Russia
- VDSina: Russian host
- Sannikov Kirill Vladimirovich (aka SANNIKOV): Russian host
- TIMEWEB-AS: Russian host
- Garant-Park-Internet LLC (aka GARANT): Russian host
- ALIBABA: Chinese host
Domains
- 76153-coinbse[.]com
- 81758-coinbse[.]com
- 81920-coinbse[.]com
- 81926-coinbse[.]com
- 81958-coinbse[.]com
- 826298-coinbse[.]com
- 83216-coinbse[.]com
- 837613-coinbse[.]com
- 83956-coinbse[.]com

