Brand Impersonation defense with Silent Push Community and Enterprise: how to combat domain, favicon, MX record and HTML title spoofing.
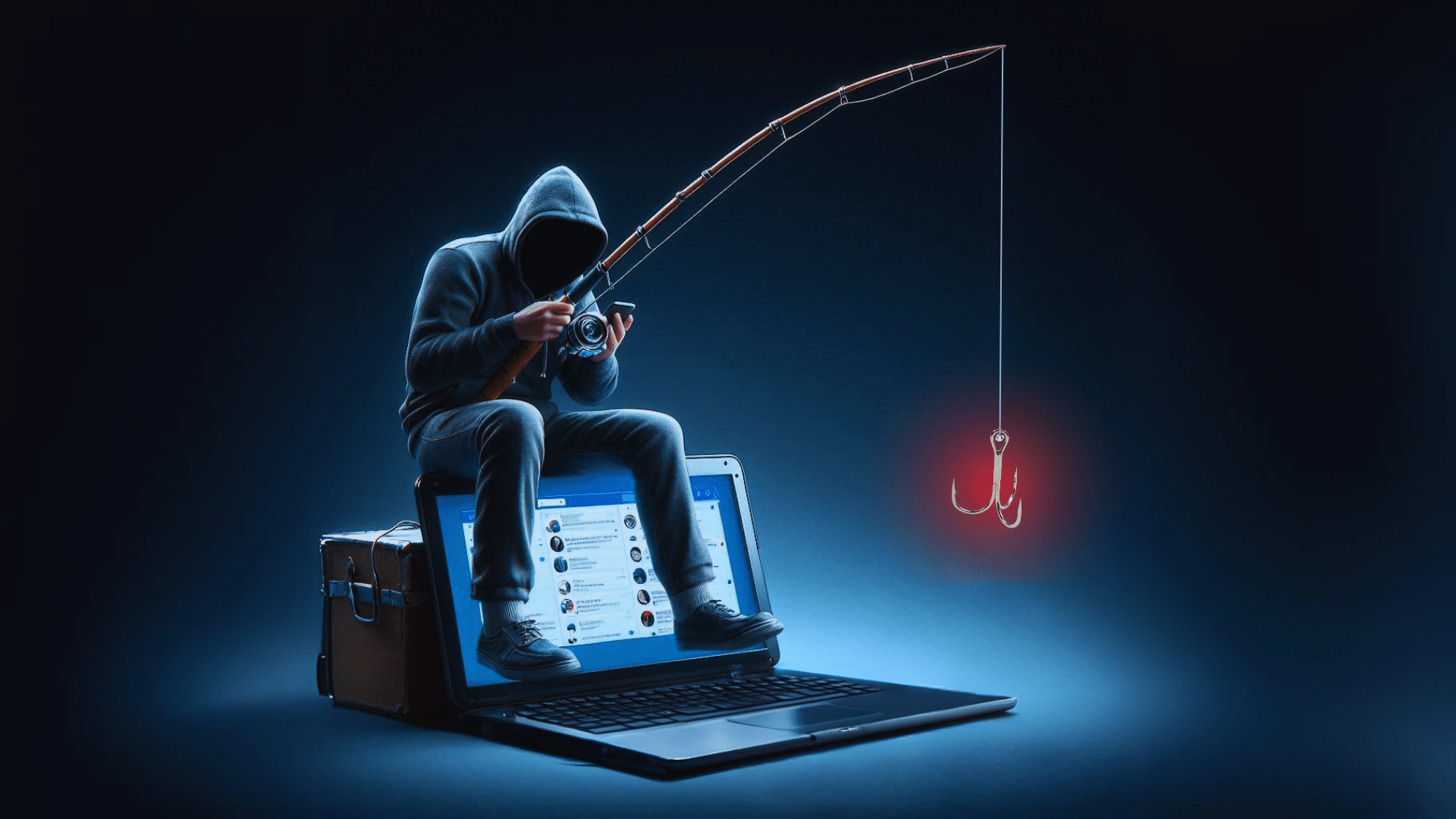

In cybersecurity terms, Brand Impersonation encompasses a variety of attacks vectors aimed at deceiving users into believing a fraudulent digital asset (usually web content, or an email) is legitimate and trustworthy.
In a typical scenario, a threat actor deploys infrastructure that spoofs a well-known brand’s website, or sends a “branded” email, with the aim of phishing for sensitive information, such as login details or payment card information, or delivering malware via an executable download.
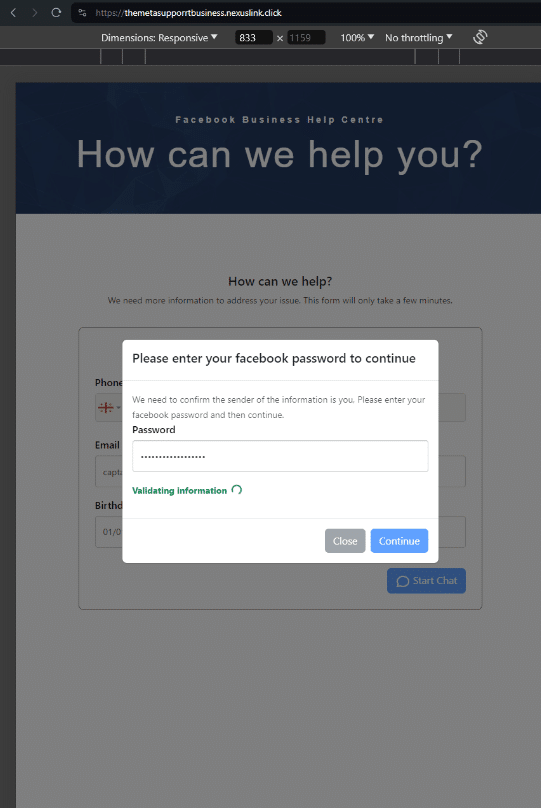
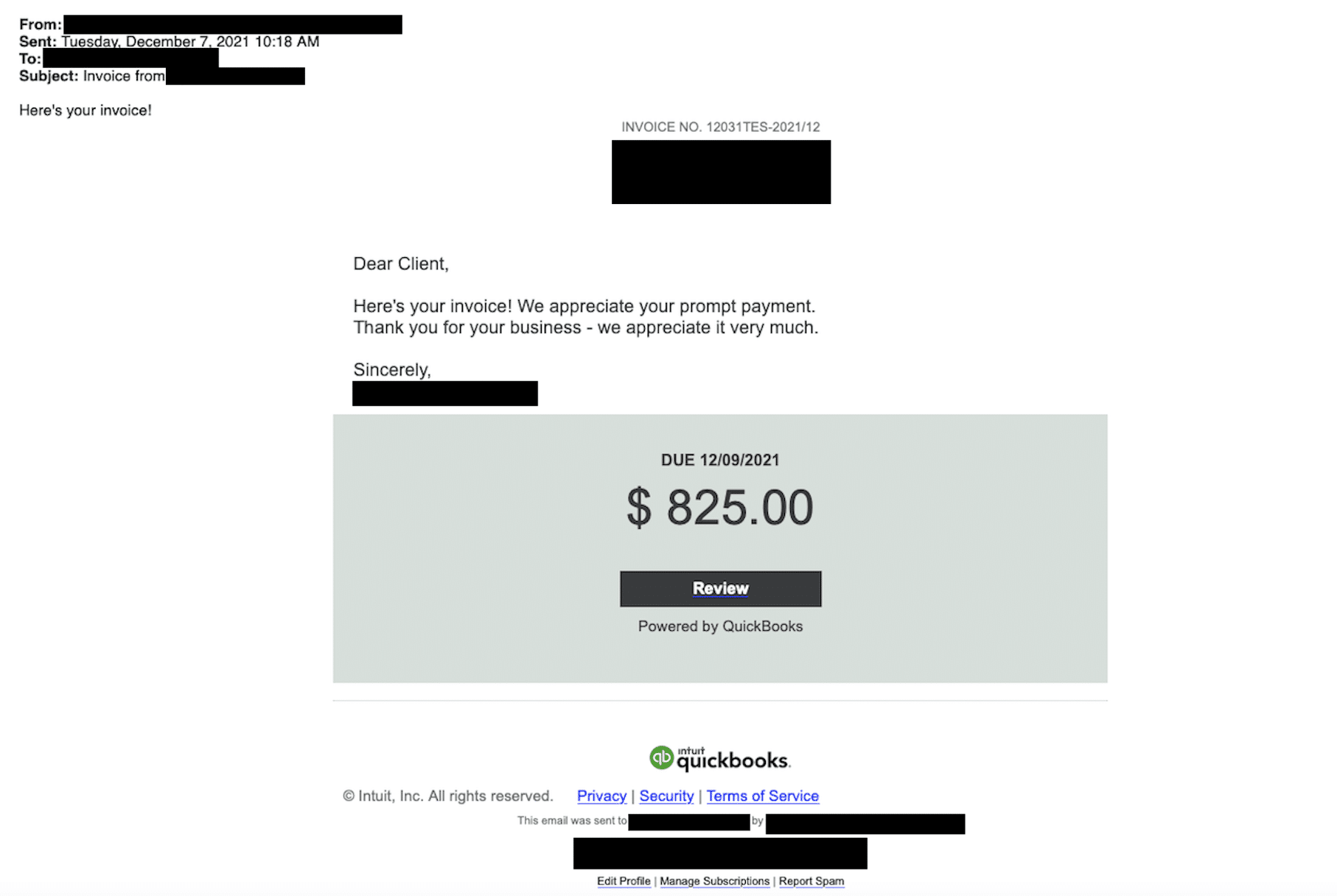
Brand Impersonation isn’t limited to on-page content or one-off emails. Threat actors also spoof individual elements of a website, such as favicons and HTML titles that appear in a browser tab, in an effort to appear legitimate to the untrained eye.
The development of commercially available AI has seen the introduction of new attacker TTPs, such as ‘deepfake’ impersonation, automated reconnaissance of digital brand assets, and dynamic machine learning adaptations to phishing messages that drastically improves spelling and grammar – previously a reliable indication of fraudulent content.
Summary
In this blog, you’ll learn how to execute four powerful Brand Impersonation queries that locate malicious Indicator of Future Attack (IOFA) infrastructure, targeting four distinct areas of your online presence:
- Domains
- Favicons
- Emails
- HTML titles
New to Silent Push? Download our free Community Edition here and follow along as we guide you through each query.
Each query generates an IOFA results set that allows security teams to track and monitor the underlying infrastructure associated with Brand Impersonation attacks, and prevent further attacks by locating additional infrastructure at source, rather than relying on post-attack intelligence.
Defenders are able to use Silent Push Brand Impersonation IOFAs to construct threat feeds dedicated to multiple apex domains or supply chain domains, ingest data into a security stack via the Silent Push API, and use enriched threat intelligence to automate their pre-breach security posture and IR processes.
Let’s take a look at each query in turn….
1. Domain Brand Impersonation query
The Silent Push Domain Impersonation query is designed to identify ‘typosquatting’ – a TTP that involves a threat actor registering a domain name that’s similar to a well-known brand, and either mispelling it or otherwise obfuscating using a combination of a subdomain and country code top level domain (ccTLD), in an attempt to capture traffic meant for a legitimate website.
From the main Domain Impersonation query screen, you can input a domain or regex – a form of advanced search that looks for specific naming patterns, instead of using whole domain names – and search for impersonating domains with one click.
To narrow the search, the query features an Auto-fill Data button that automatically excludes results hosted on trusted infrastructure (the IP, subnet, nameserver and ASN associated with your legitimate domain). You can also manually include or exclude certain infrastructure.
You can use the First Seen and Last Seen sliders to focus on recent impersonation attempts, or execute a historical interval-based search using Silent Push’s passive DNS records.
Working with Domain Impersonation results
Domain Impersonation results are generated on an Explore screen – the standard output screen for DNS data across Silent Push Enterprise and Community Editions – alongside their associated risk score.
From the Explore screen, you can perform further forward and reverse DNS pivots on any domain or IP address returned, you can enrich any ASN you discover to explore malicious clusters of domains and IPs, and as with any dataset on the Explore screen you can save all or a section of the results to a new or existing feed.
2. Email Brand Impersonation query
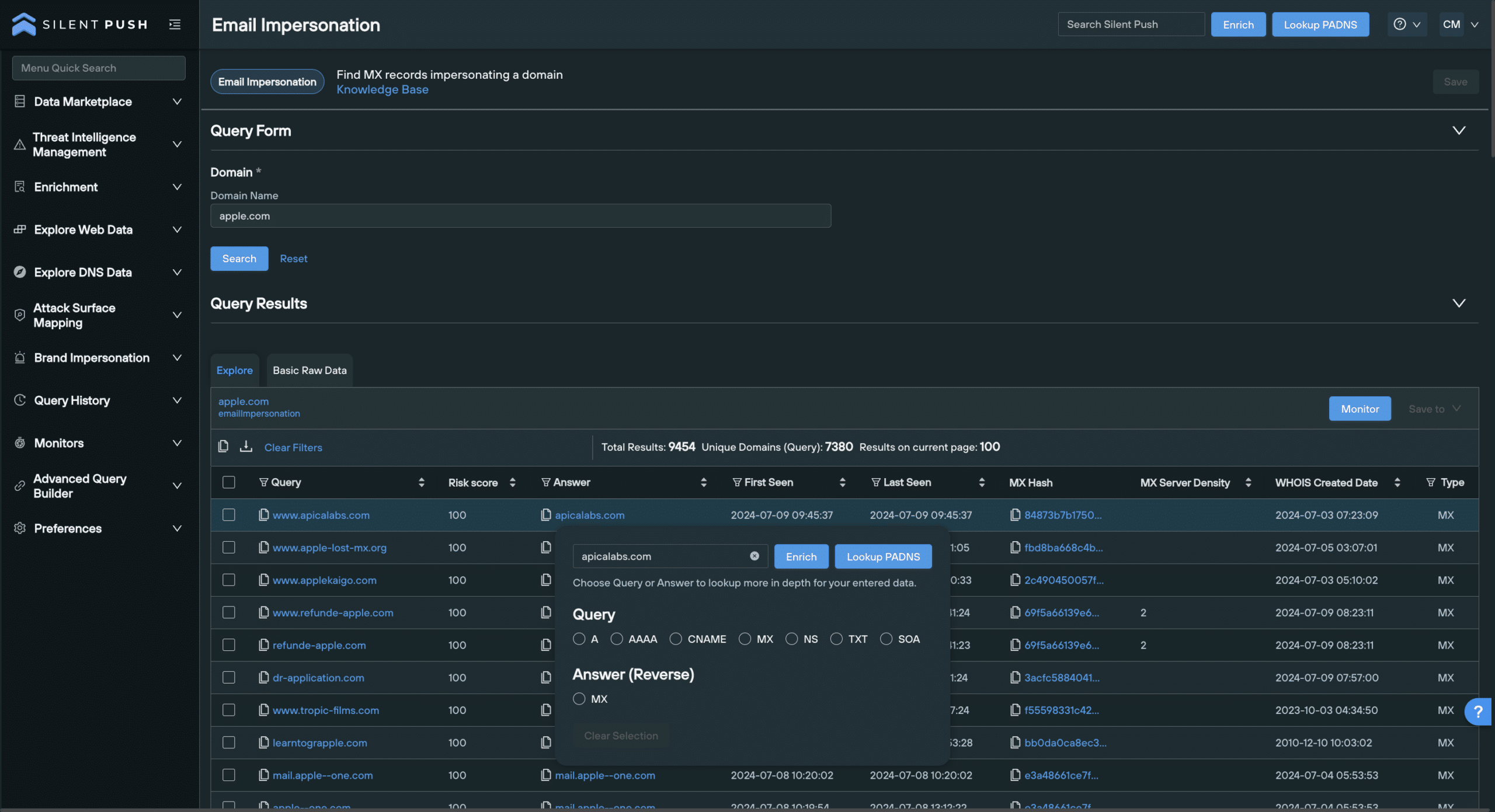
Our Email Impersonation feature locates domains that are being used to target organizations through MX record manipulation.
MX (Mail Exchange) records are DNS instructions that dictate which mail server is responsible for receiving emails for a specific domain.
By manipulating these records, attackers can make it appear as though their emails are coming from a legitimate sender’s mail server, despite originating from a malicious source.
The Email Impersonation query returns both mail records and their associated domains that are potentially involved in impersonation attacks against your own infrastructure.
Working with Email Impersonation results
Data is returned across the following categories, along with associated risk scores:
Querycontains the potentially suspect domainAnsweris the MX record that the domain is pointing toMX Hashis a hash value associated with the MX record listed in the Answer columnWHOIS Createdis a timestamp of when the domain in the Query column (and its subdomains) was createdMX Server Densityis the number of domains using the returned mailserver
Results are populated on an Explore screen. You can click any string of blue text to perform additional forward and reverse DNS pivots on domains and MX records, or enrich a piece of data by viewing granular information across 100+ constituent categories.
3. Favicon Brand Impersonation query
Favicons are small images (usually 16×16 pixels), unique to each brand, that appear in browser tabs, address bars, bookmarks and search engine results.
Replicating a brand’s favicon and linking it to a spoofed website is a relatively straightforward task, and threat actors use them to make phishing infrastructure appear legitimate in the eyes of the user, increasing the believability of their scam.
The Silent Push Favicon Impersonation query captures favicon data associated with a trusted domain, and hunts for non-trusted malicious infrastructure using the same favicon image.
Simply enter a domain, and click Search to locate spoofed infrastructure.
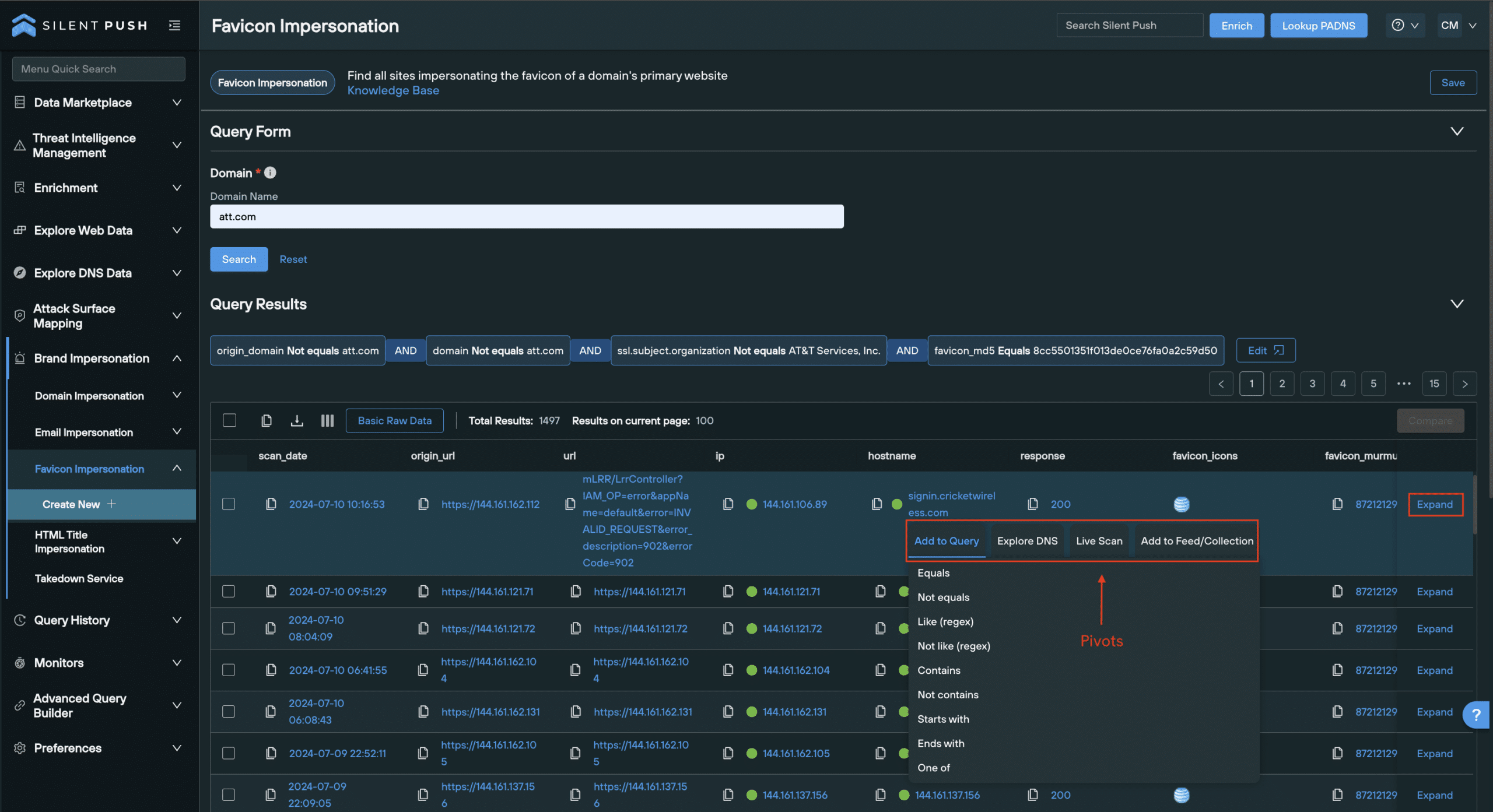
Working with Favicon Brand Impersonation results
Favicon Impersonation queries are executed on the back-end using Silent Push Web Scanner.
When a Favicon Impersonation query is run, the platform automates a Web Scanner query that captures the MD5 hash of a domain’s legitimate favicon, and automatically scans for its use across all public-facing non-trusted infrastructure.
Unlike Domain Impersonation and Email Impersonation queries, Favicon Impersonation results are populated using a Web Scanner table, with the following default categories:
scan_date– Timestamp of when the data was scannedorigin_url– URL that was originally scannedURL– The final destination URLhostname– Domainfavicon_icons– Image displaying the favicon retutned for that resultfavicon_murmur3– Murmur3 hash (standard favicon)favicon2_murmur3– Murmur3 hash (favicon2)
Web Scanner is powered by SPQL, a free-form query language used to explore all the DNS data and content gathered by our daily scans of the Internet’s IPv4/6 range, and the dark web. SPQL utilizes 100+ data categories, including SSL data, redirects, HTML header data, and body hash values.
Data categories can be added or removed from the Favicon Impersonation results table depending on how much you’d like to know about a returned domain. Simply click the icon next to Basic Raw Data, and select or deselect categories from the list.
To get a comprehensive breakdown of each result, including all relevant SPQL field names associated with the result, click Expand on the far right of the results table.
As with the Explore table used to provide Domain Impersonation and Email Impersonation results, you can pivot on any string of blue text to perform a variety of additional functions and gather more intelligence, including:
- Add a result to a new Web Scanner query
- Perform a Live Scan of a URL
- Add a domain or IP address to a feed
- Enrich a piece of data, or perform a passive DNS lookup
HTML Title Brand Impersonation query
A HTML title is the text string that appears in your browser tab, or a website’s title bar.
As with favicon spoofing, threat actors use HTML titles to make their impersonation infrastructure appear legitimate.
Fake websites masquerading as a well-known brand will often feature what appears to be a legitimate HTML title in their website code, so that casual visitors are fooled into thinking the domain is safe and secure.
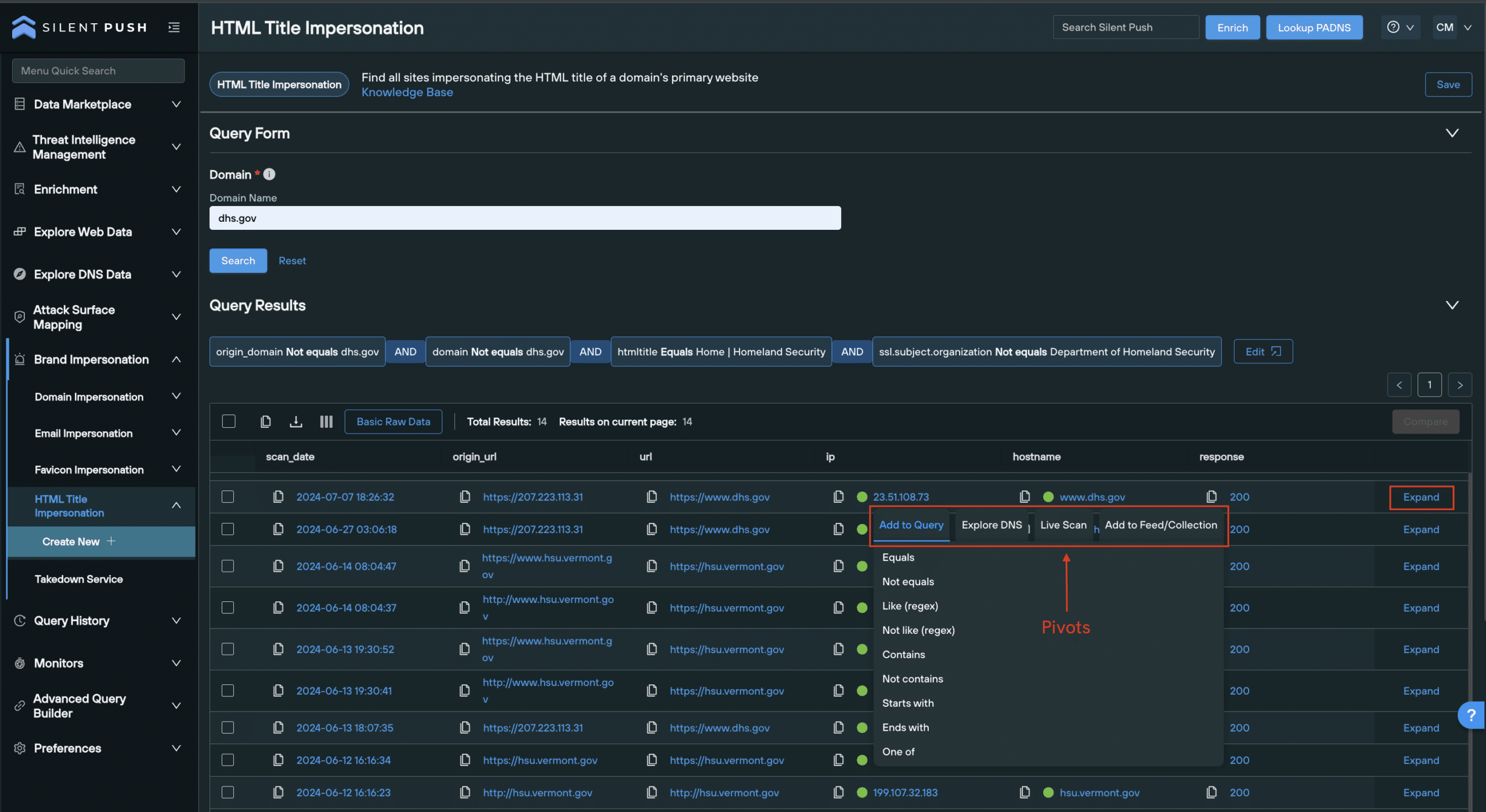
To run a query, simply enter a trusted domain and hit Search.
Working with HTML Title Impersonation results
Just like a Favicon Impersonation queries, HTML Title queries use Web Scanner to capture the legitimate domain’s HTML title, and run a query that locates non-trusted domains using the same HTML title.
Results are populated across the following default columns:
htmltitle– HTML title of the returned resultscan_date– Timestamp of when the data was scannedorigin_url– URL that was originally scannedURL– The final URL that’s arrived atIP– IP addresshostname– Domain
As with Favicon Impersonation data, the results table can be adjusted according to what you need to know.
You can add data categories that provide more content to each malicious domain returned, expand on each result to get a comprehensive breakdown of a domain’s constituent parts, or pivot across infrastructure using Enrichment and passive DNS lookups.
Monitoring queries
Silent Push allows you to setup Brand Impersonation Monitors that alert you to changes in a given dataset via email, every 24 hours.
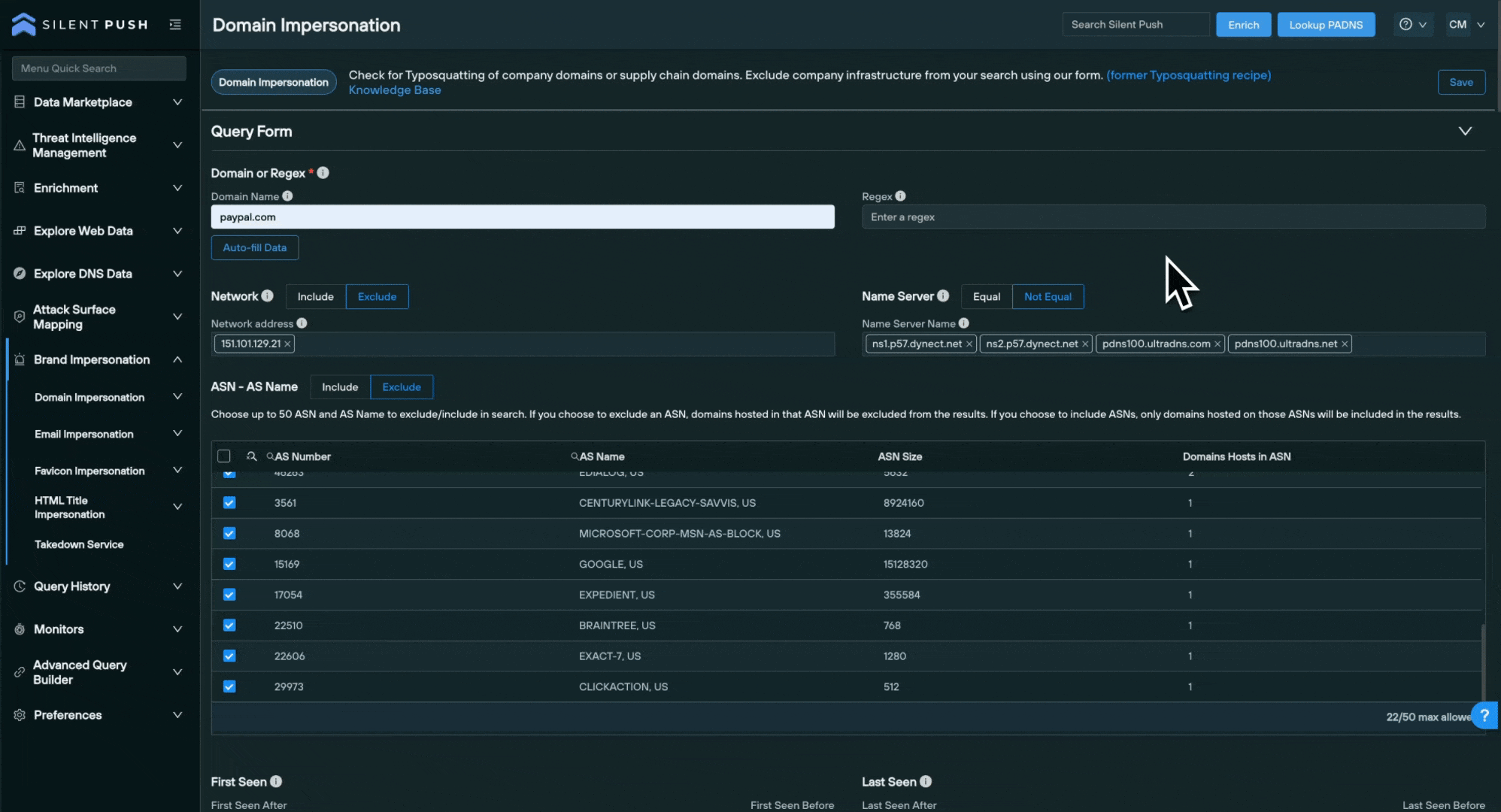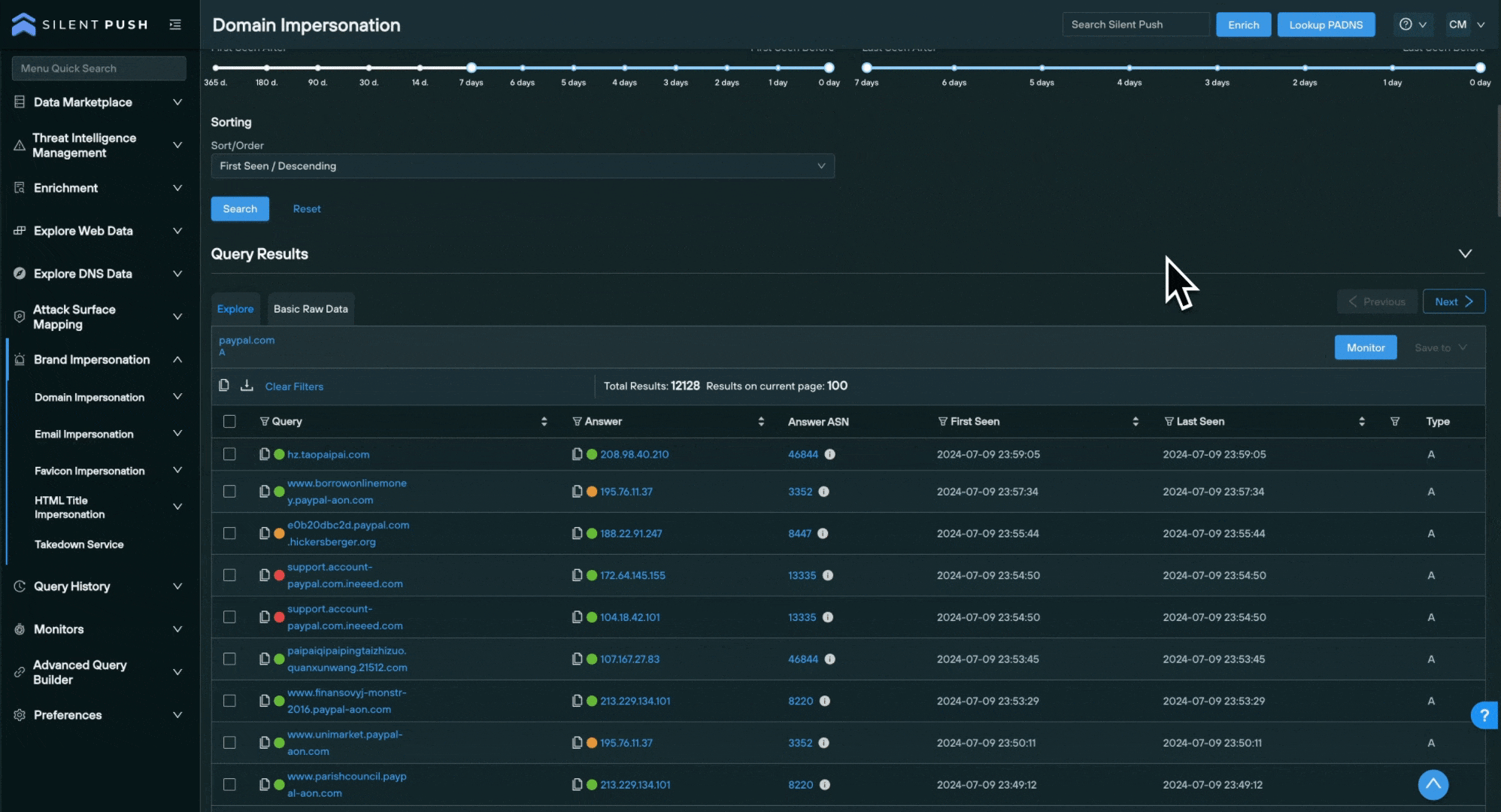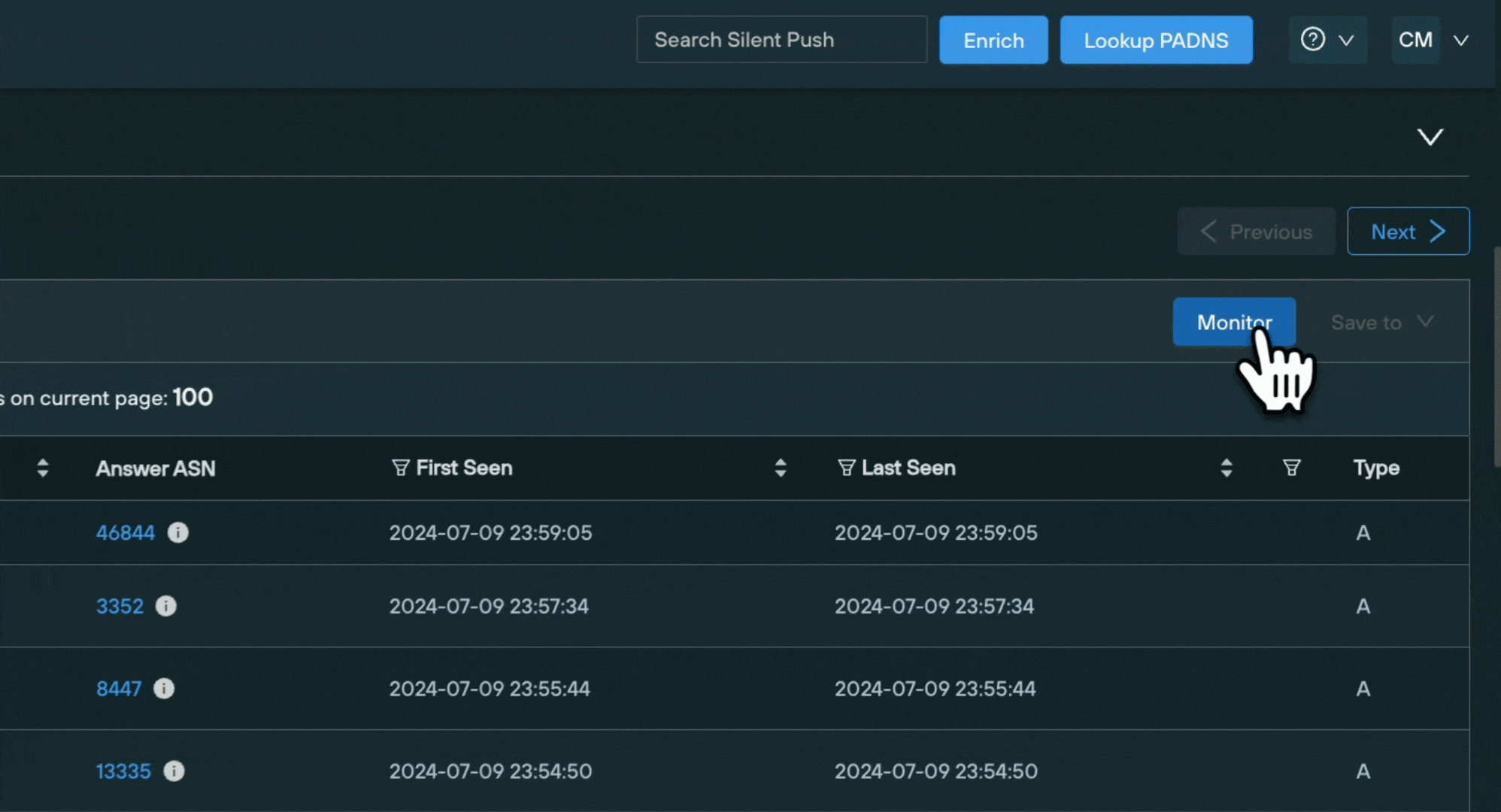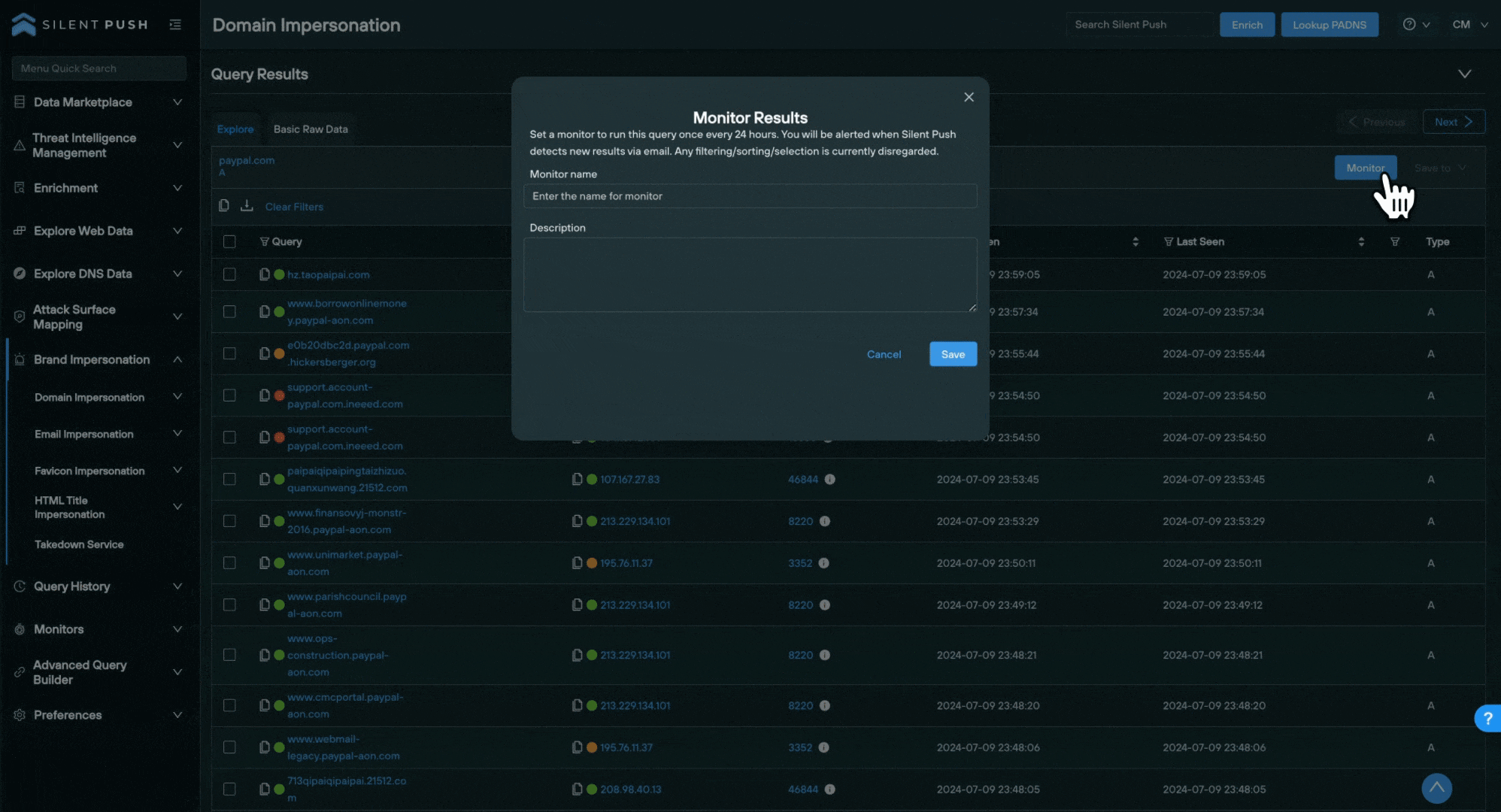
To create a Monitor:
- Select the Monitor button on the top right of the results screen.
- Enter a Monitor Name and a Description.
- Click Save.
Monitors can be accessed, edited and deactivated by navigating to Monitors > Monitored Queries.
You can also save your queries for quick access at a later date, or share them across your organization with other team members.
Register for Silent Push Community Edition
You can access all the Brand Impersonation features detailed in this blog using Silent Push Community Edition – a free threat hunting and cyber defense platform used by security teams, researchers and threat hunters across the globe, in a variety of sectors.
Community Edition also features access to Silent Push Web Scanner and Live Scan, along with a variety of powerful DNS lookups, and offensive/defensive tooling.
Sign-up free here.


